Proctitis
378
Learn about proctitis: its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for rectal inflammation to help manage discomfort effectively.

Proctitis - Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
What is Proctitis?
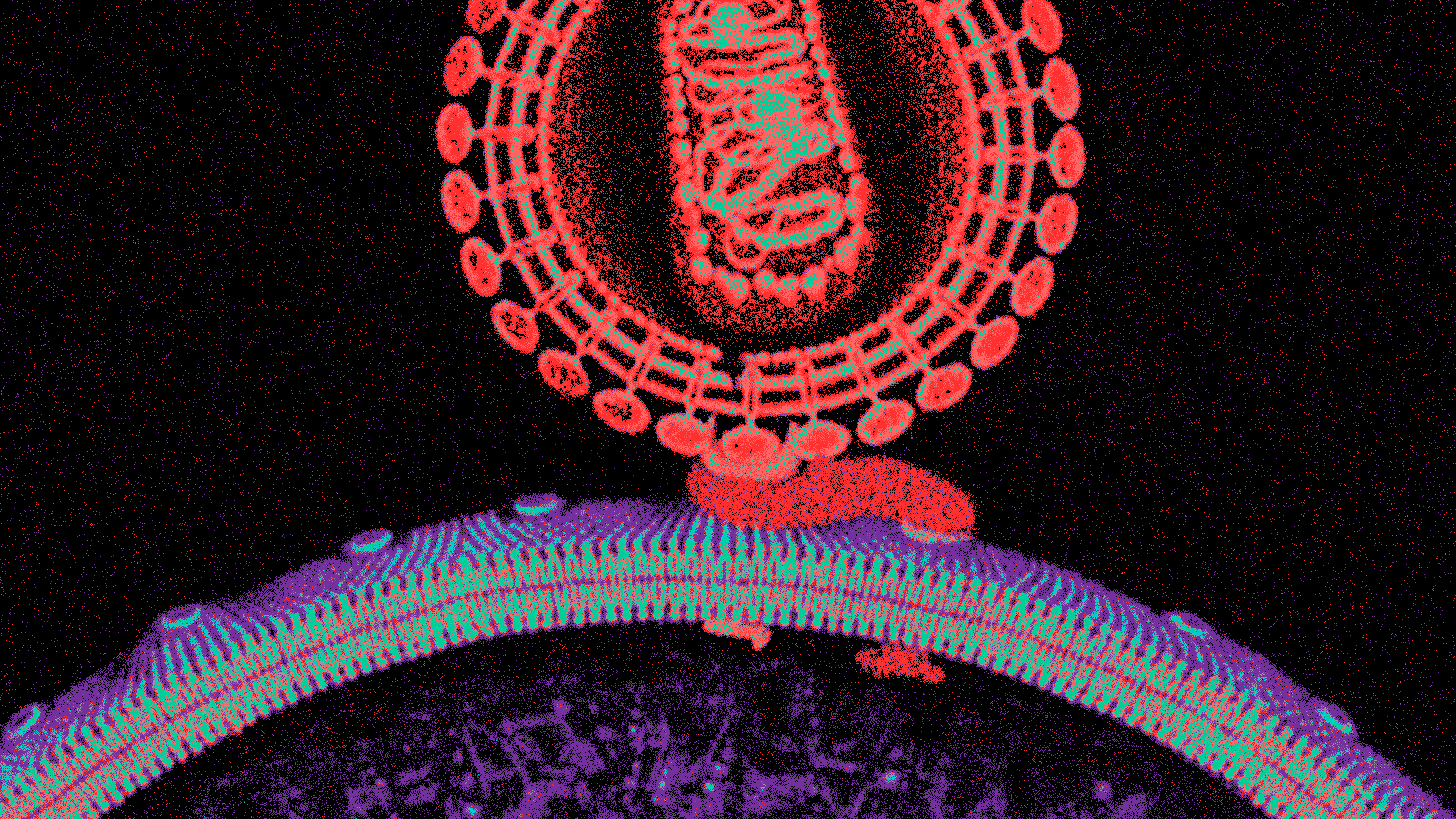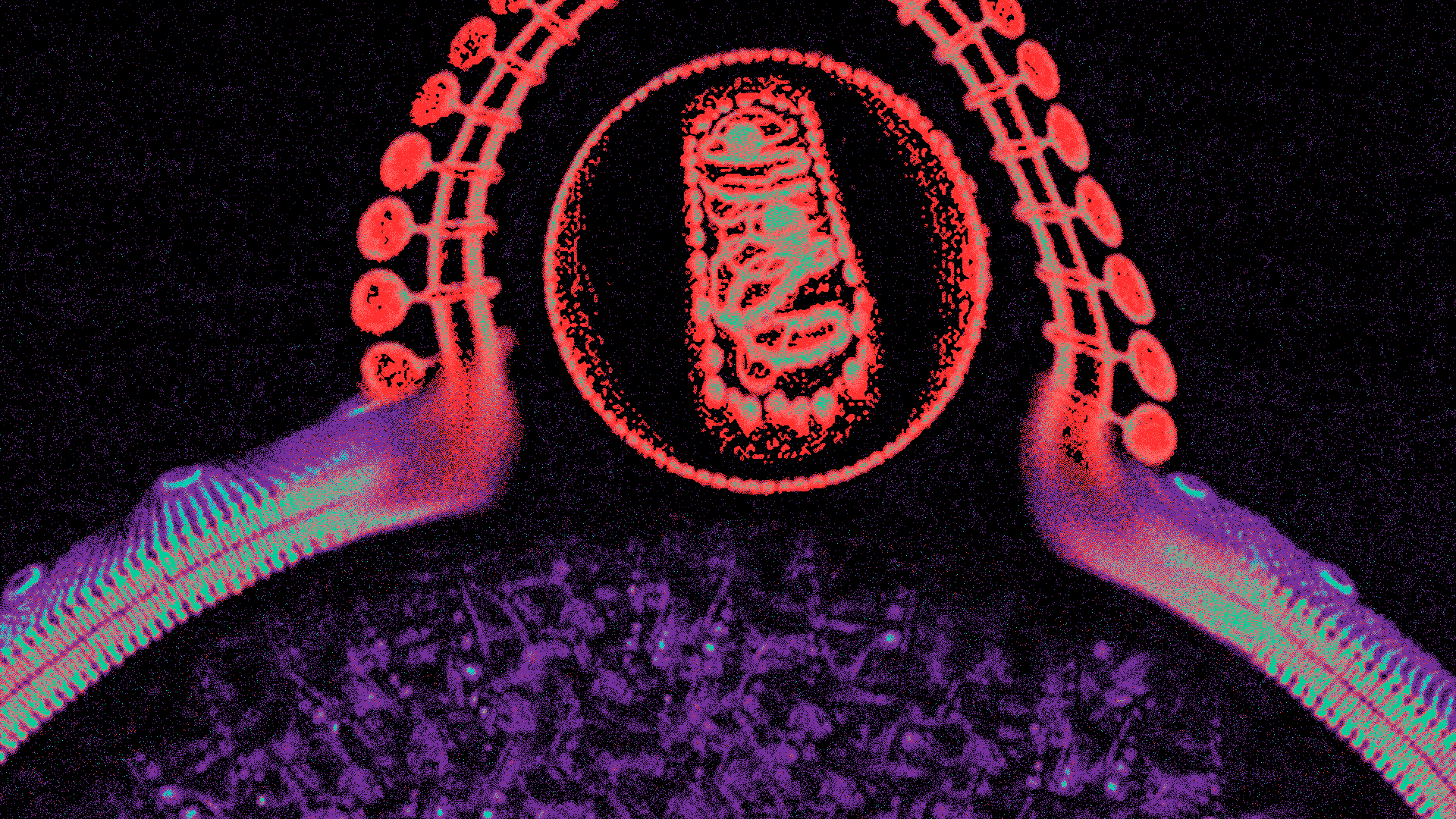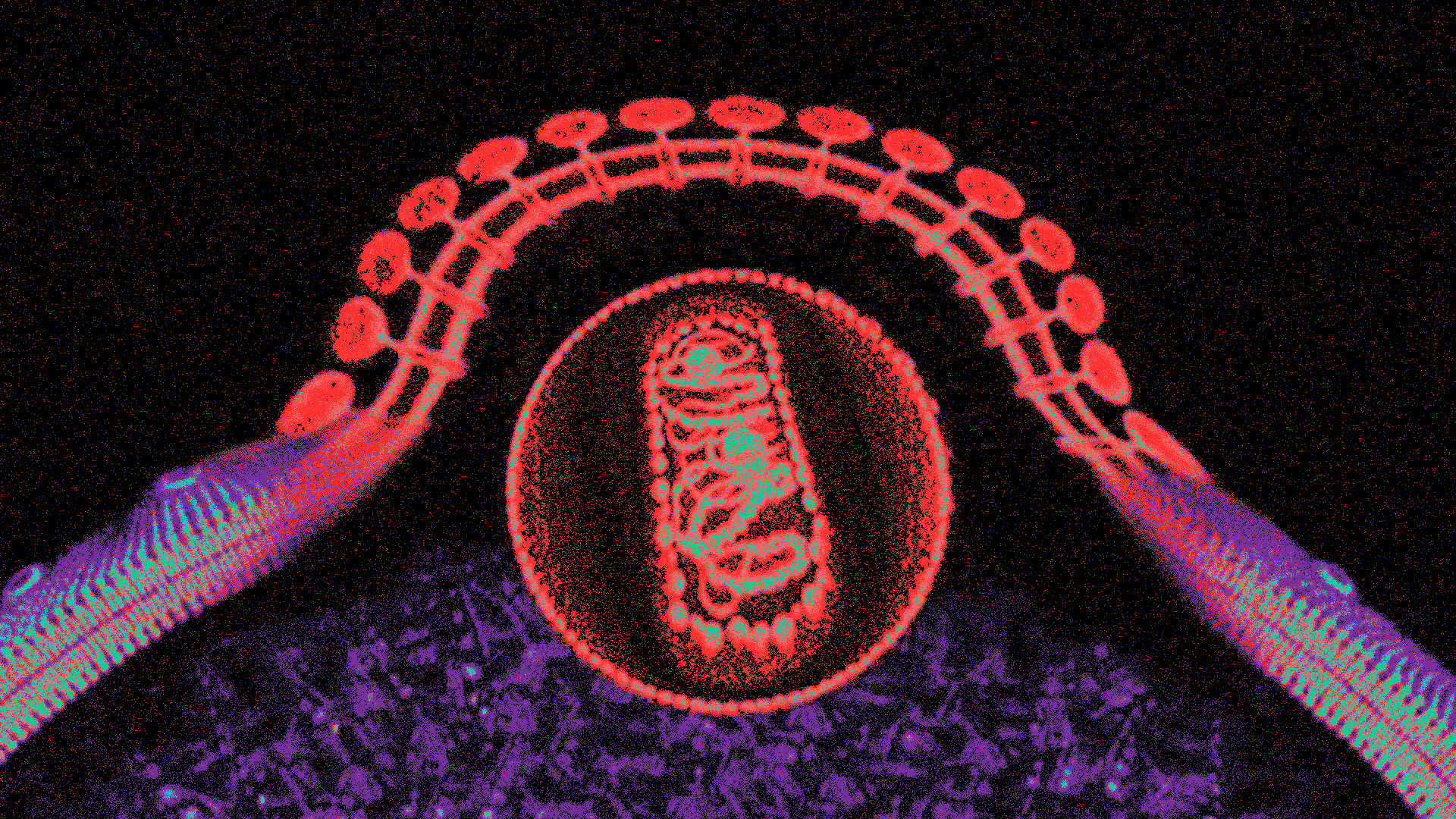
Proctitis is the inflammation of the rectum, the final section of the large intestine. This condition can lead to discomfort, pain, and a range of gastrointestinal symptoms. Proctitis can occur in isolation or as part of other gastrointestinal disorders, and its severity can vary from mild to severe.
What Causes Proctitis?
The causes of proctitis can be classified into several categories:
1. Infectious Causes
- Bacterial Infections: Certain bacteria, such as those causing sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like gonorrhea or chlamydia, can lead to proctitis.
- Viral Infections: Viruses like cytomegalovirus (CMV) or herpes simplex virus (HSV) may cause inflammation.
- Parasitic Infections: Parasites such as Entamoeba histolytica can also lead to proctitis.
2. Inflammatory Conditions
- Ulcerative Colitis: A form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that primarily affects the colon and rectum, often causing proctitis as part of its presentation.
- Crohn’s Disease: Another type of IBD that can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, including the rectum.
3. Radiation Therapy
- Proctitis can occur as a side effect of radiation therapy for cancers in the pelvic region, such as prostate or cervical cancer.
4. Allergic Reactions
- Allergic reactions to certain medications or substances can lead to inflammation of the rectum.
5. Other Causes
- Sexual Activity: Certain sexual practices, especially anal intercourse, can irritate the rectum and contribute to proctitis.
- Chemical Irritation: Exposure to irritants such as soaps, douches, or other hygiene products can result in inflammation.
Proctitis Symptoms
The symptoms of proctitis can vary based on the underlying cause but commonly include:
- Rectal Pain or Discomfort: This may range from mild irritation to severe pain.
- Bleeding: Blood may appear in the stool or on toilet paper after a bowel movement.
- Diarrhea: Frequent loose stools can occur, sometimes accompanied by urgency.
- Mucus Discharge: Increased mucus may be present in the stool.
- Tenesmus: A feeling of incomplete bowel evacuation, leading to a persistent urge to defecate.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing proctitis typically involves:
- Medical History: Discuss symptoms, potential exposures, and any relevant medical conditions.
- Physical Examination: A digital rectal exam can help assess the condition of the rectum.
- Laboratory Tests: Stool tests may be conducted to identify infections or inflammatory markers.
- Endoscopy: A sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy may be performed to visually inspect the rectum and collect tissue samples if needed.
Treatment Options
The treatment for proctitis depends on its underlying cause:
1. Medications
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections, antibiotics can effectively treat the underlying cause.
- Antivirals: In cases of viral infections, antiviral medications may be necessary.
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: Corticosteroids or 5-ASA (aminosalicylic acid) medications can reduce inflammation in cases related to inflammatory bowel disease.
2. Dietary Changes
- Modifying the diet may help alleviate symptoms. High-fiber diets can promote regular bowel movements, while avoiding irritants like spicy foods may be beneficial.
3. Sitz Baths
- Taking warm sitz baths can provide relief from discomfort and help soothe inflammation in the rectal area.
4. Avoiding Irritants
- Identifying and avoiding irritants, such as harsh soaps or certain hygiene products, can help prevent further irritation.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience symptoms of proctitis, especially persistent pain, bleeding, or changes in bowel habits, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Contact us at info.bkk@pulse-clinic.com or chat on your preferred platform:
![]() +66 65 237 1936
+66 65 237 1936  @PULSEClinic
@PULSEClinic ![]() PulseClinic
PulseClinic
Conclusion
Proctitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the rectum, resulting in discomfort and various gastrointestinal symptoms. Understanding its causes and recognizing the symptoms can lead to timely diagnosis and effective treatment. If you experience signs of proctitis, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice to address the condition and find relief.
Trust PULSE CLINIC to take care of your health like other 45000 people from over 130 countries. We provide discreet professional service with high privacy. Here to help, not to judge.
I have my prescription and I want to order now, TAKE ME THERE !
Loading...
Clinic Locations
Loading...